190
saia-pcd.com
KNX
KNX
S-Net
S-Bus
S-IO
Communication & interaction
h
Serial protocols with standard interfaces
h
IP-based protocols
h
Dedicated communications systems
IP-based protocols are mainly used for connecting controllers to management systems.
IP protocols are also used to exchange data between automation devices and with local
control devices. For example, BACnet is very good for communicating between automation
devices and the management system. Web and IT services such as DHCP, DNS, SNTP, SNMP
and SMTP (emails) have proven themselves in the integration of automation devices into the
IT infrastructure. Web-based visualisations with suitable web servers and a CGI-bin interface
in the automation device also provide a sustainable basis for operation and service over the
entire life-cycle of a system.
Field components mainly use serial protocols fitted with standardised interfaces such as
RS-232, RS-485 or RS-422. Despite the low baud rate, these interfaces have the advantage
over Ethernet by being simple to install. The cable and infrastructure components such as
repeaters are cheaper than a complete IT infrastructure. Field bus systems are also easier to
service and maintain.
For certain field devices it is practical to use a dedicated hardware interface. Such systems are
optimised for a particular task. DALI is suitable for controlling lighting, for example, and
M-Bus is designed for connecting meters. However, these systems should not be used for
communication between automation stations.
2.1
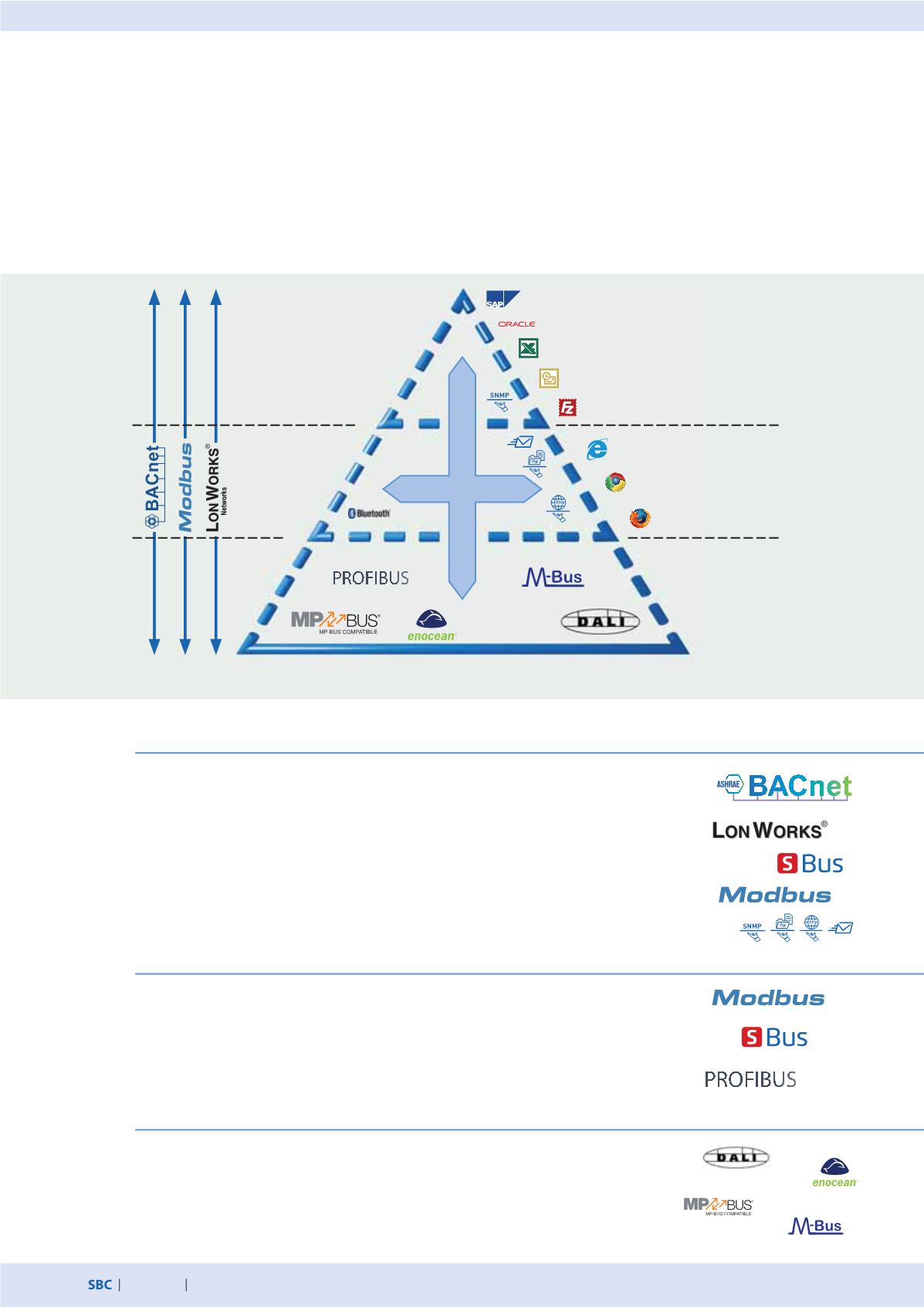
The basic features of Saia PCD® communications systems
Saia PCD® systems provide communication protocols suitable for all layers of the automation pyramid in order to integrate
a PCD into the communication infrastructure of a building. In addition to performing regulation and control tasks, the PCD
is often used for connecting different systems from different building services. Irrespective of the type of interface, using only
standardised communications systems is recommended for heterogeneous systems. From experience, compatibility
and sustainability are better solved using standard technologies than closed solutions of a single manufacturer. The following
diagram illustrates the essential differences between communications systems, from the field to the management layer.
Numerous protocols can be used simultaneously across all layers.
Management layer
Automation layer
Field level


