13
saia-pcd.com
I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
►
►
►
►
►
5
Switch cabinet
components
4
Consumer
data acquisition
3
Dedicated
room controllers
2
Operation
and monitoring
1
Automation
stations
Automation stations – the basics
A user program may contain various data types. This includes data that is relevant for a fast regulation process and data
records that must be collected over a long period or saved permanently. All these data types have different requirements
in terms of hardware. For example, a regulation-relevant process requires a fast memory to calculate and provide current
values. However, historical data records require sufficient remanent mass memory to cover a long period of time.
Memory management in the Saia PCD® systems
If a user program function is placed in PG5,
various memory areas are required in the
system. These areas can basically be divided
into 3 groups. The parameter group controls
the behaviour of the FBox that is processed
in the user program. Defined statuses of the
parameters result in responses in the FBox.
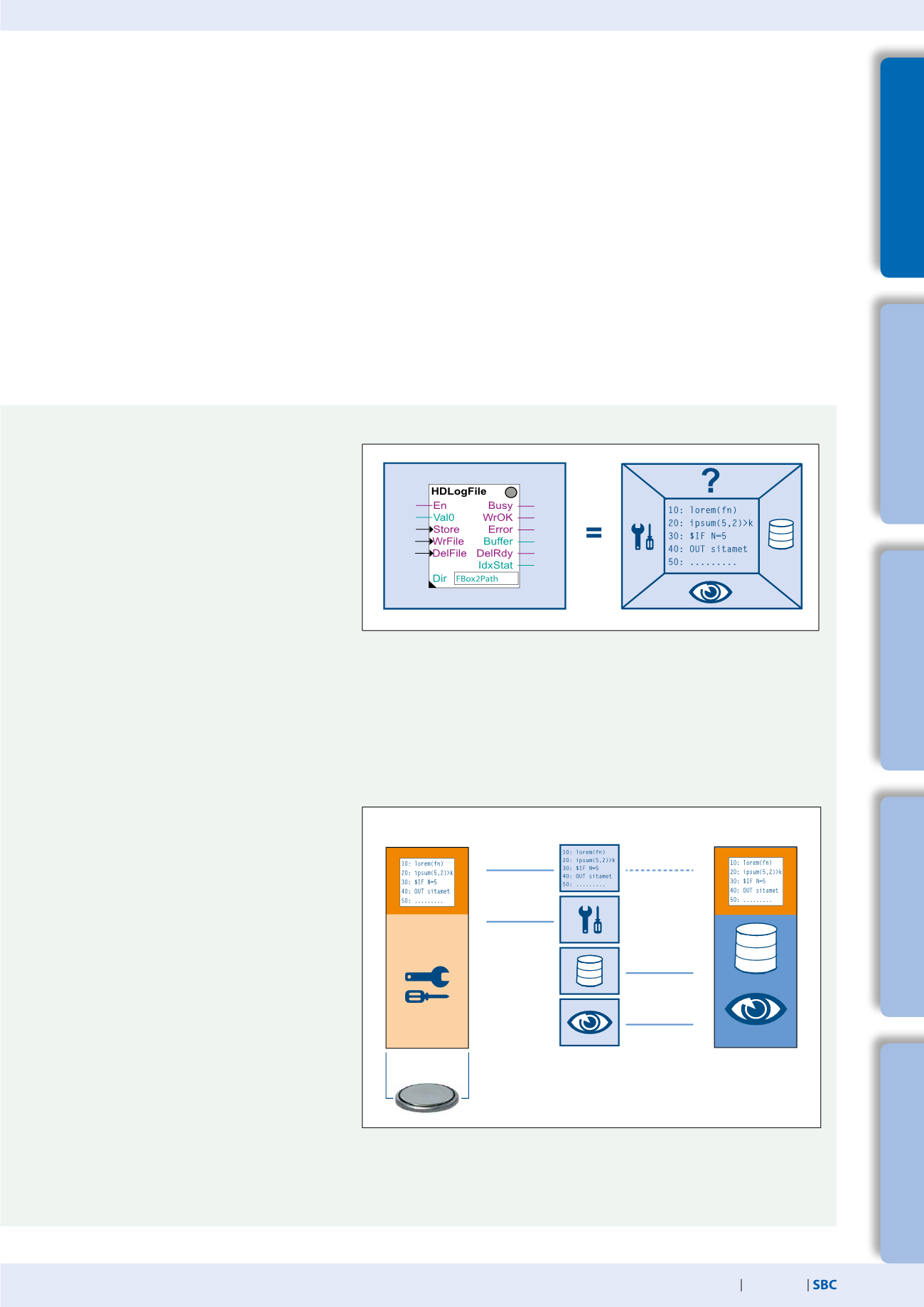
Using the example of the HDLog function,
the log data of the associated parameters
is written to the file system in an Excel-
compatible file format. Various templates are
provided in the Web Editor to visualise this
file in the web application.
These can be easily connected to the FBox
using a range of parameters. As the visualisa-
Saia PG5® FBox shown as an object in the Saia PG5® Fupla engineering environment.
To the right you can see which functions belong to the object.
This is how the functions of a memory area belonging to the Saia PG5® FBox are mapped.
Memory areas of the Saia PCD® systems
A distinction is made between two key
memory areas.
The user memory, which ensures fast access
for reading and writing, contains time-criti-
cal content such as media and the program
code executed by the CPU. However, this
memory is not a programmable read-only
memory (PROM) and is buffered by a bat-
tery.
The flash memory, on the other hand, per-
manently saves data and provides space for
historical data records or data that will not
change during the operation of the system.
The backup of the user application can be
stored in a file system, which means that the
processing of teh program is guaranteed.
tion pages only change when the Saia PG5® project is created, these are stored in
the file system.
Visualisation
Log data
Code
Code
Parameters
RAM
Flash memory


